Deploying Flink CDC Jobs with Docker compose
Running Apache Flink containers using Docker Compose is a convenient way to get up and running to try out some Flink workloads.
You can start out using a docker compose file, then upload and run an SQL file that contains the jobs you want to run.
This approach of running workloads on Flink is using Flink SQL, it’s one of several ways to run workloads. Writing Java apps, compiling them as Jar files and uploading them to run is probably the more common way to run workloads.
Here is a minimal docker compose file to run a Flink job manager and 2 task managers
version: '3.7'
services:
jobmanager:
image: flink:1.17.1
environment:
- JOB_MANAGER_RPC_ADDRESS=jobmanager
ports:
- "8081:8081"
command: jobmanager
taskmanager:
image: flink:1.17.1
environment:
- JOB_MANAGER_RPC_ADDRESS=jobmanager
depends_on:
- jobmanager
command: taskmanager
deploy:
replicas: 2
Assuming docker compose is installed you can start the containers using the following command in the same folder as the docker compose file:
docker compose up -d
This will start the containers in the background and you can check that the containers are running using
docker ps
You should see something like the following showing a jobmanager and 2 task managers.
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
eb87408560be flink:1.17.1 "/docker-entrypoint.…" 35 minutes ago Up 35 minutes 6123/tcp, 8081/tcp apache_flink_and_docker_compose-taskmanager-2
565fd52d250a flink:1.17.1 "/docker-entrypoint.…" 35 minutes ago Up 35 minutes 6123/tcp, 8081/tcp apache_flink_and_docker_compose-taskmanager-1
0b3e3eaa5c06 flink:1.17.1 "/docker-entrypoint.…" 35 minutes ago Up 35 minutes 6123/tcp, 0.0.0.0:8081->8081/tcp, :::8081->8081/tcp jobmanager
To start adding some work to Flink you can access the Flink console using the following command and from there you can try out various jobs like creating tables.
Use the docker-compose.yml file in this repo to create Flink, Mariadb and redis containers instead of the minimal example provided earlier.
docker exec -it jobmanager /opt/flink/bin/sql-client.sh

To get a feel for using Flink, create a table that will read data from a database table running in another container:
-- read in the data from the table in mariadb
CREATE TABLE sales_records_table (
sale_id INT,
product_id INT,
sale_date DATE,
sale_amount DECIMAL(10, 2),
PRIMARY KEY (sale_id) NOT ENFORCED
) WITH (
'connector' = 'mysql-cdc',
'hostname' = 'mariadb',
'port' = '3306',
'username' = 'root',
'password' = 'rootpassword',
'database-name' = 'sales_database',
'table-name' = 'sales_records'
);
The view the data using:
select * from sales_records_table;
If you want to take things up a notch, you can write your SQL commands to a file, then submit the file to Flink for it to run in the background.
The following file has a few commands to read from a fictional log of sales in a table in a source database, perform ongoing change data capture (CDC), perform a sum of all sales and then sink the resulting sales sum in to redis.
-- read in the data from the table in mariadb
CREATE TABLE sales_records_table (
sale_id INT,
product_id INT,
sale_date DATE,
sale_amount DECIMAL(10, 2),
PRIMARY KEY (sale_id) NOT ENFORCED
) WITH (
'connector' = 'mysql-cdc',
'hostname' = 'mariadb',
'port' = '3306',
'username' = 'root',
'password' = 'rootpassword',
'database-name' = 'sales_database',
'table-name' = 'sales_records'
);
-- create a view that aggregates the sales records
CREATE TEMPORARY VIEW total_sales AS
SELECT
SUM(sale_amount) AS total_sales_amount
FROM
sales_records_table;
-- create a redis sink table
CREATE TABLE redis_sink (
key_name STRING,
total DECIMAL(10, 2),
PRIMARY KEY (key_name) NOT ENFORCED
) WITH (
'connector' = 'redis',
'redis-mode' = 'single',
'host' = 'redis',
'port' = '6379',
'database' = '0',
'command' = 'SET'
);
-- insert the aggregated sales records into the redis sink table
INSERT INTO
redis_sink
SELECT
'total_sales',
total_sales_amount
FROM
total_sales;
This job.sql will already be available in the container ready to run it:
docker exec -it jobmanager /opt/flink/bin/sql-client.sh embedded -f job.sql
While this is a made up example its a good example of what Flink can do on its own.
Once the Job is running, check the Flink UI and you’ll see your running Job by going to http://localhost:8081/#/overview
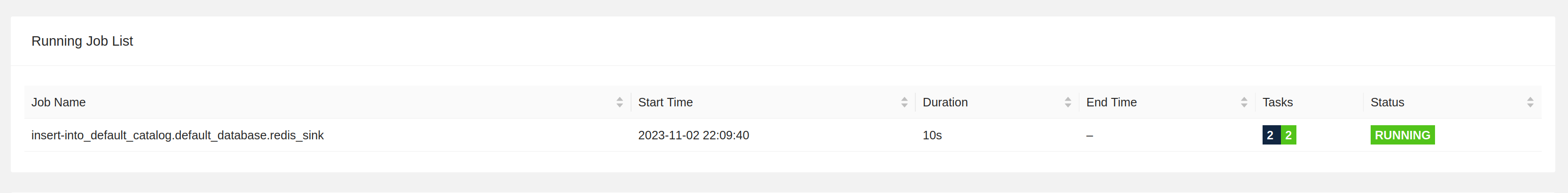
You can check redis to see if the value is in there:
redis-cli -h localhost
get total_sales
# "5500.00"
You can expand on this by adding Checkpoints, which can be handy to help Flink jobs tolerate restarts. I wrote about checkpoints recently here: https://gordonmurray.com/data/2023/10/25/using-checkpoints-in-apache-flink-jobs.html
Once you’re done, you can run docker compose down to stop the containers.